Introduction to Aplastic Anemia
Aplastic anemia is a rare blood disorder that affects the bone marrow and its ability to produce blood cells. As someone who has done extensive research on this topic, I know just how devastating this condition can be. In this article, we will explore what aplastic anemia is, its symptoms, and the various treatment options available. By understanding this disorder, we can better support those who are affected by it.
Understanding the Role of Bone Marrow in Blood Cell Production
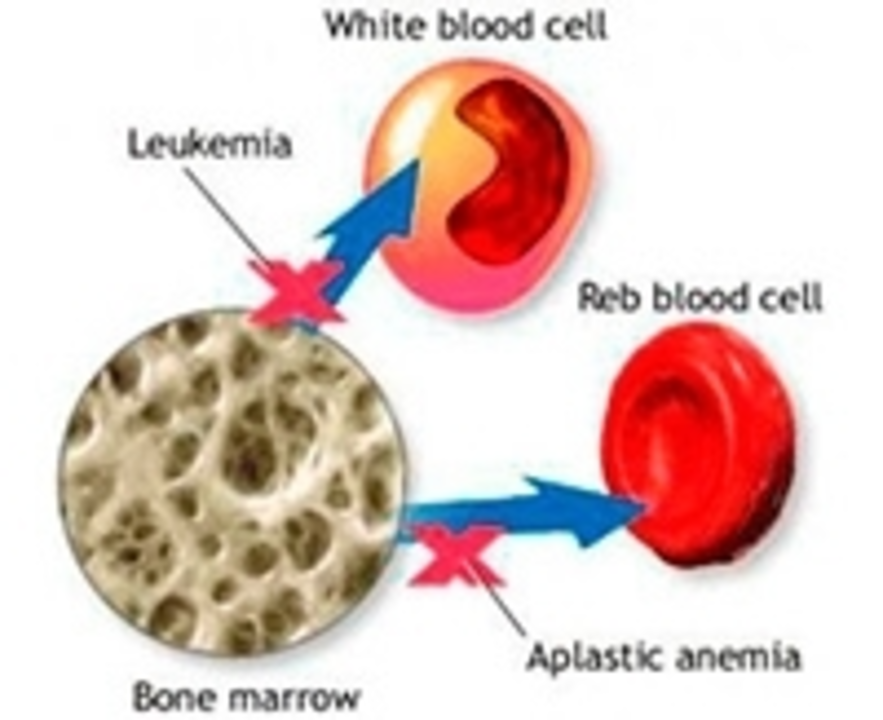
Before diving into the specifics of aplastic anemia, it's important to understand the role of bone marrow in blood cell production. Bone marrow is a spongy tissue found within our bones, and it's responsible for producing three types of blood cells: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These cells are essential for our body's overall functioning, as they carry oxygen, fight infections, and help with clotting.
When a person has aplastic anemia, their bone marrow is damaged and becomes unable to produce enough blood cells. This leads to a deficiency in all three types of blood cells, causing a wide range of symptoms and health problems. The exact cause of this damage can vary, but it often involves the immune system attacking the bone marrow or exposure to certain chemicals or radiation.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Aplastic Anemia
Because aplastic anemia affects the production of all three types of blood cells, the symptoms can be quite diverse. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Fatigue and weakness due to a lack of red blood cells (anemia)
- Frequent infections and slow recovery from illnesses due to a lack of white blood cells (leukopenia)
- Easy bruising and bleeding due to a lack of platelets (thrombocytopenia)
Other symptoms that may be present include pale skin, shortness of breath, rapid heart rate, and dizziness. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosing Aplastic Anemia
If a doctor suspects that a patient has aplastic anemia, they will typically begin with a thorough evaluation of the patient's medical history and a physical examination. Blood tests will also be conducted to check for low blood cell counts and to rule out other possible causes of the symptoms.
If the initial tests suggest aplastic anemia, the doctor may recommend a bone marrow biopsy. This procedure involves taking a small sample of bone marrow from the hip bone and examining it under a microscope. A bone marrow biopsy can provide valuable information about the overall health of the bone marrow and can help confirm the diagnosis of aplastic anemia.
Exploring Treatment Options for Aplastic Anemia
Once a diagnosis of aplastic anemia is confirmed, the doctor will discuss treatment options with the patient. The choice of treatment will depend on several factors, including the severity of the condition, the patient's age, and their overall health. Some of the most common treatment options include:
- Blood transfusions to temporarily increase blood cell counts
- Immunosuppressive therapy, which uses medications to suppress the immune system and reduce its attack on the bone marrow
- Stem cell transplantation, in which healthy bone marrow cells from a donor are transplanted into the patient's body to replace the damaged bone marrow
In some cases, additional treatments may be needed to manage specific symptoms or complications of aplastic anemia, such as antibiotics for infections or medications to control bleeding.
Living with Aplastic Anemia
Managing aplastic anemia can be challenging, but with the right treatment and support, many people are able to lead fulfilling lives. It's important for patients and their loved ones to work closely with their healthcare team to develop a personalized care plan that addresses both physical and emotional needs. This may include regular medical appointments, ongoing treatment, and lifestyle modifications to reduce the risk of infections and other complications.
Connecting with others who have experience with aplastic anemia can also be helpful. Support groups, online forums, and organizations like the Aplastic Anemia and MDS International Foundation can provide valuable resources, information, and emotional support for those living with this rare blood disorder.
Conclusion
Aplastic anemia is a rare and challenging blood disorder that can have a significant impact on a person's life. By understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, we can better support those affected by this condition and help them live their best lives possible. Remember, if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of aplastic anemia, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.

Helena Pearson
Life throws curveballs, and aplastic anemia is one of those daunting ones.
Feeling the weight of a rare blood disorder can be overwhelming, but remember there’s a community ready to lift you up. 🌟
Keep your spirit resilient and lean on supportive networks; they can turn the tide of isolation into hope. 🌈
Stay vigilant with your health checks and never underestimate the power of a kind word.